Introduction
USDCAD is the short form for the US dollar against the Canadian dollar. USDCAD, just like the EURUSD, GBPUSD, AUDUSD, etc. is a major currency pair. In this pair, the US dollar is the base currency, and the Canadian dollar is the quote currency. Trading this currency pair is known as trading the “loonie” because it is the name for the Canadian one-dollar coin.
Understanding USD/CAD
The exchange price of USD/CAD is basically the value of 1 USD in terms of CAD. It is quoted as 1 US dollar per X* Canadian dollars. For example, if the value of USDCAD is 1.3300, it means that it takes 1.3300 Canadian dollars to buy one US dollar.
*X is the current market price of USDCAD
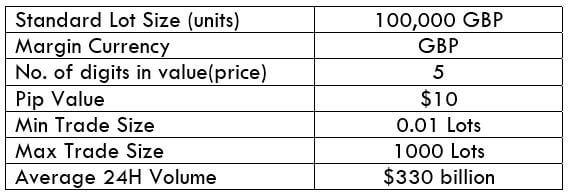
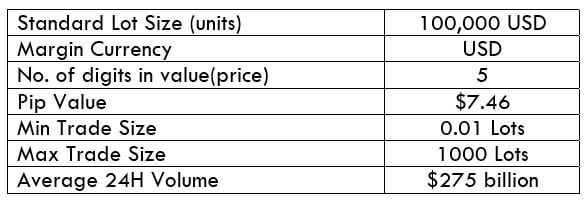
USD/CAD Specification
Spread
The difference between the bid price and the ask price mentioned by the broker is the spread. Typically, this differs from the type of account.
Spread on ECN: 0.7
Spread on STP: 1.2
Fees
There is a fee (commission) on every trade a trader takes. This again depends on the type of account registered by the user. There is no fee on the STP account, but a few pips on an ECN account.
Note: We are considering fees in terms of pips, not currency units.
Slippage
Sometimes a trader is executed at a different price from what he had intended. This variation in price is known as slippage. Slippage takes place when orders are executed as a market type, and it depends on the volatility of the currency pair and also the execution speed of the broker.
Trading Range in USD/CAD
Trading analysis is not all about predicting when the prices will rise and fall. Sometimes, even though a trader knows the prices are going to rise/fall, it might not be ideal to jump on the trade without the knowledge of volatility of the market. Volatility range plays a major role in managing the total cost of a trade. Hence, it is vital to know the minimum, average, and maximum pip movement in each timeframe to assess the trading costs.
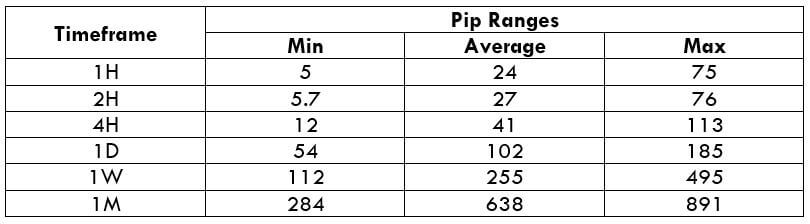
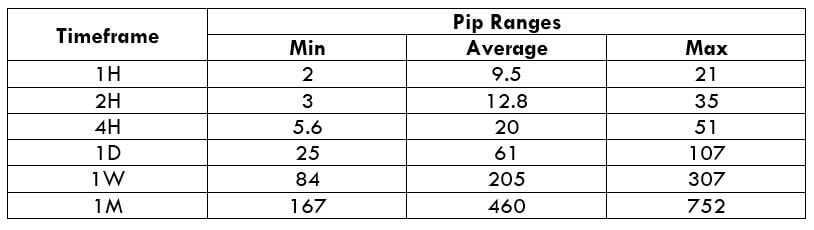
Below is a table that depicts the minimum, average, and maximum volatility (pip movement) on different timeframes.
USD/CAD PIP RANGES
Procedure to assess Pip Ranges
- Add the ATR indicator to your chart
- Set the period to 1
- Add a 200-period SMA to this indicator
- Shrink the chart so you can assess a large time period
- Select your desired timeframe
- Measure the floor level and set this value as the min
- Measure the level of the 200-period SMA and set this as the average
- Measure the peak levels and set this as Max.
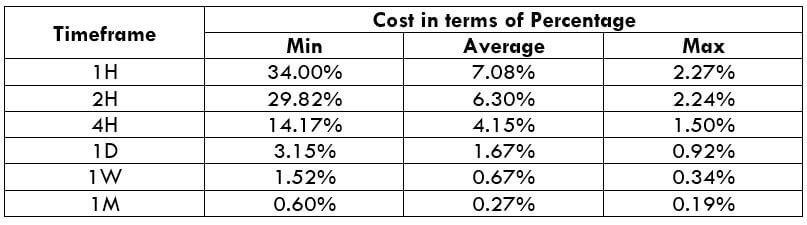
USD/CAD Cost as a Percent of the Trading Range
With the min, average, and max pip movement, the cost range is calculated in terms of percentage. This percentage has no unit and determines if the width of the cost. That is, if the percentage is high, the cost is high for the trade, and if the percentage is low, the cost is low too.
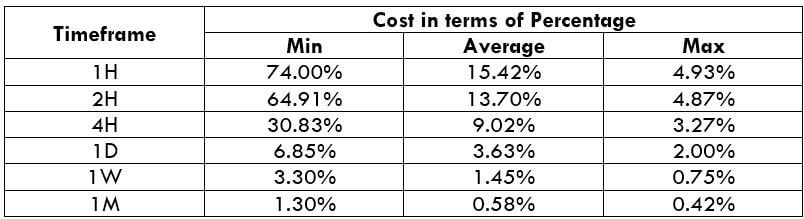
Below are two tables representing the range of cost for an ECN account and an STP account.
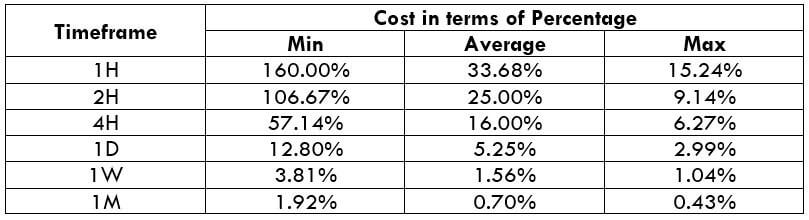
ECN Model Account
Spread = 0.7 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 1
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 0.7 + 1 = 3.7
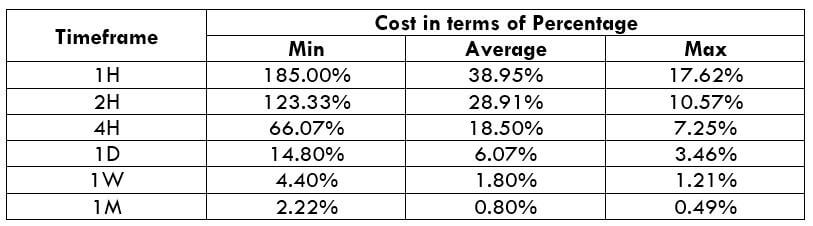
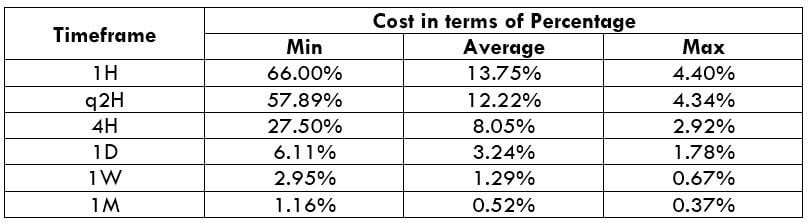
STP Model Account
Spread = 1.2 | Slippage = 2 | Trading fee = 0
Total cost = Slippage + Spread + Trading Fee = 2 + 1.2 + 0 = 3.2
The Ideal way to trade the USD/CAD
As mentioned earlier, the higher the percentage, the higher is the cost for a trade. Applying this idea to the above tables, it can clearly be inferred that the percentages are high on the minimum column. This means that the costs are high when the volatility of the currency pair is very feeble.
Similarly, the costs are considerably low when the volatility is quite high. However, this does not mean that trading during high volatility is the ideal way. This is because the volatility is quite risky to trade volatile markets. Therefore, one must trade during those times of day when the market volatility is around the mentioned average. The costs are decent enough, and the risk is maintained just fine.
Another point of consideration is that costs are reduced significantly when the slippage is made nil. This can be made possible by entering and exiting a trade by placing a pending/limit order instead of executing them by market.
Below is the same cost percentage table after making the slippage value to 0.
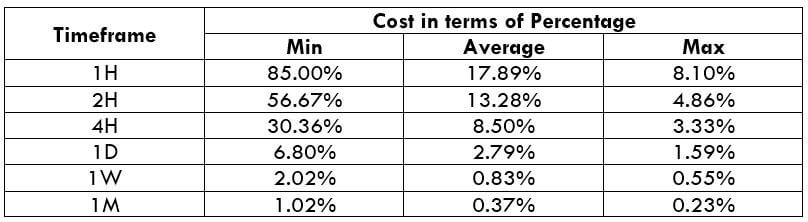
Now it is evident from the above table that slippage eats up a significant amount of cost on each trade. Hence, limit orders are the way to go.